When you look at your computer, whether it’s a desktop or a laptop, it might just seem like a sleek, functional machine that gets the job done. But behind its shiny exterior lies a collection of powerful components working together to perform a variety of tasks. Understanding the basics of computer hardware can help you make informed decisions when buying or upgrading your system, troubleshoot problems, and even help you customize a build tailored to your needs. In this article, we’ll take a look at the key components that make up a computer and what each part does.

1. Central Processing Unit (CPU) – The Brain of Your Computer
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is often referred to as the “brain” of your computer. It’s responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations that power every program, app, and action you perform on your PC.
What It Does:
- Processing Instructions: The CPU carries out the instructions of a program by performing basic arithmetic, logic, and input/output operations.
- Coordinates with Other Components: It communicates with other hardware components (such as RAM and storage) to perform tasks.
What to Look For:
When choosing a CPU, consider factors such as:
- Clock Speed: Measured in gigahertz (GHz), clock speed indicates how fast the processor can execute instructions.
- Cores: Modern CPUs have multiple cores (dual-core, quad-core, etc.), which allow for better multitasking and performance in demanding tasks.
- Threads: Threads are the number of tasks a CPU can perform simultaneously. More threads generally mean better multitasking ability.
2. Motherboard – The Backbone of Your PC
The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects and allows communication between all the components in your computer. It houses the CPU, memory (RAM), storage devices, and various expansion cards.
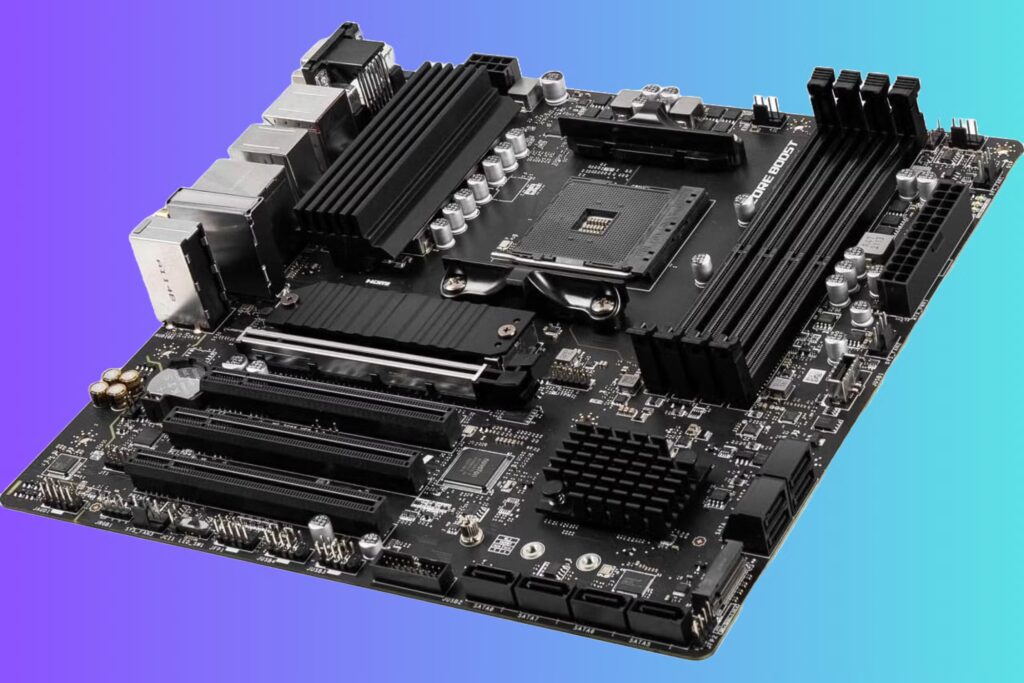

What It Does:
- Connects Components: The motherboard has slots and connectors for various components like the CPU, RAM, hard drives, and GPU (graphics card).
- Power Distribution: It distributes power to all the connected components via the power supply unit (PSU).
What to Look For:
- Socket Type: Make sure the motherboard is compatible with the CPU you plan to use. Different CPUs have different socket types.
- Form Factor: The motherboard comes in different sizes (ATX, micro-ATX, etc.), so ensure it fits within your case.
- Expansion Slots: These slots allow you to add additional components like a graphics card or sound card.
3. Random Access Memory (RAM) – Short-Term Memory
RAM is a type of computer memory that is used to store data temporarily while the CPU is working on it. It is often referred to as “short-term memory” because it holds data that the computer needs to access quickly.
What It Does:
- Stores Active Data: RAM stores data for active processes and tasks. The more RAM your computer has, the more programs and data it can handle simultaneously.
- Boosts Speed: The more RAM available, the faster your computer can run applications and perform tasks without slowing down.
What to Look For:
- Capacity: For general use, 8GB of RAM is usually sufficient. For gaming, video editing, or heavy multitasking, aim for 16GB or more.
- Speed: RAM speed (measured in MHz) affects data transfer between the RAM and CPU, with higher speeds leading to faster performance.
- Dual Channel: Two sticks of RAM in a dual-channel configuration will generally improve performance over a single stick.
4. Storage – Where Your Data Lives
There are two main types of storage in modern computers: Hard Disk Drives (HDD) and Solid State Drives (SSD).

HDD (Hard Disk Drive):
- What It Does: HDDs store data magnetically on spinning disks. They’ve been around for decades and are commonly found in budget systems.
- Pros: HDDs offer a larger storage capacity at a lower price.
- Cons: Slower read and write speeds compared to SSDs.
SSD (Solid State Drive):
- What It Does: SSDs use flash memory to store data, with no moving parts, making them much faster and more durable than HDDs.
- Pros: SSDs provide faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and improved overall system responsiveness.
- Cons: They are more expensive per gigabyte of storage compared to HDDs.
What to Look For:
- Capacity: For SSDs, 256GB is typically the minimum for a primary drive. For HDDs, 1TB or more is common for data storage.
- Speed: SSDs come in different types, such as SATA and NVMe (faster and more efficient). If you’re using an SSD for your primary drive, NVMe is a good choice.
5. Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) – The Heart of Visuals
The GPU is responsible for rendering graphics and video. It’s a crucial component for gaming, video editing, and any task that requires high-quality visuals.
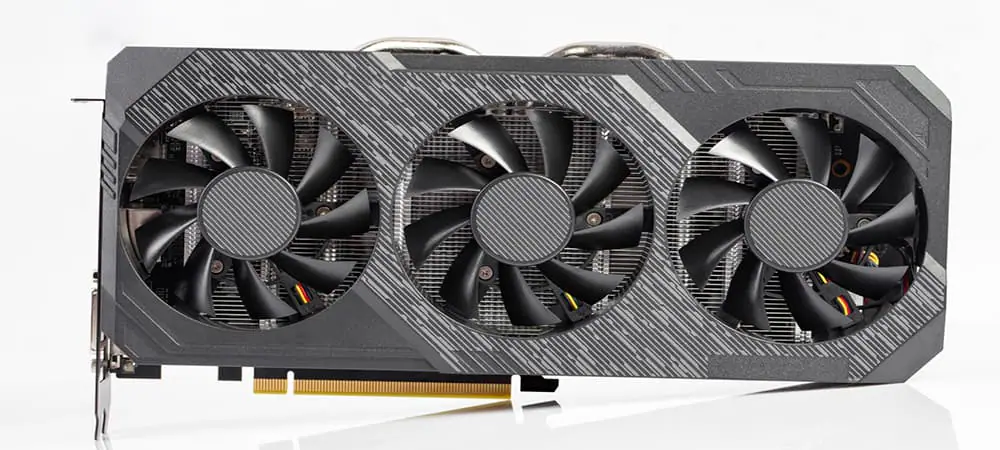

What It Does:
- Graphics Rendering: The GPU processes and renders images, animations, and video. It works alongside the CPU, taking care of the heavy lifting when it comes to graphics-heavy tasks.
- Gaming & Multimedia: For gaming, a powerful GPU will provide better frame rates, smoother gameplay, and enhanced visual fidelity.
What to Look For:
- VRAM (Video RAM): VRAM is the memory dedicated to graphics processing. 4GB of VRAM is generally sufficient for gaming, but higher amounts are necessary for tasks like 4K gaming or 3D rendering.
- Brand: The two main GPU manufacturers are Nvidia and AMD. Nvidia’s GeForce and AMD’s Radeon series are both popular choices, depending on your needs and budget.
6. Power Supply Unit (PSU) – The Lifeblood of Your PC
The PSU is responsible for delivering power to all the components of your computer. It converts electricity from your wall outlet into usable power for the system.
What It Does:
- Distributes Power: The PSU distributes power to your motherboard, CPU, GPU, storage devices, and other components.
- Regulates Voltage: It ensures the correct voltage is provided to each component, helping maintain system stability and preventing damage.
What to Look For:
- Wattage: Make sure the PSU provides enough wattage to power all your components. Higher-end systems with powerful CPUs and GPUs may require 600W or more.
- Efficiency Rating: Look for a PSU with an 80 Plus certification, which indicates energy efficiency and helps reduce energy waste and heat.
7. Cooling System – Keeping Things Cool
The cooling system in your computer prevents it from overheating. Computers generate heat, and if the temperature gets too high, it can cause damage to internal components.
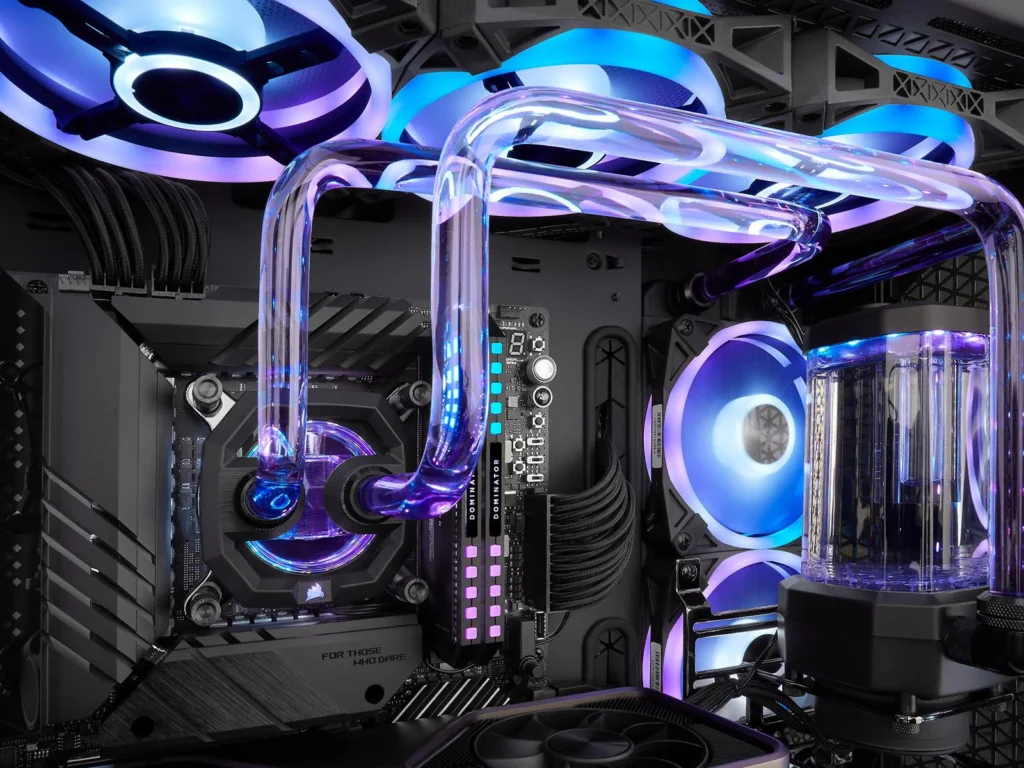

What It Does:
- Regulates Temperature: The cooling system keeps the CPU, GPU, and other components at optimal temperatures using fans or liquid cooling systems.
- Improves Longevity: Proper cooling extends the lifespan of your computer by preventing thermal damage.
What to Look For:
- Fans: Most computers come with built-in fans for cooling. Larger cases and higher-end systems may require additional fans or liquid cooling solutions.
- Thermal Paste: Ensures proper heat transfer from the CPU or GPU to the heatsink.
Conclusion
Inside your PC lies an intricate collection of components, each playing a vital role in ensuring the system runs efficiently. From the CPU, which handles the computations, to the GPU, which powers your visuals, every piece works together to make your computer function as a cohesive unit. Whether you’re building your own PC or buying a pre-built system, understanding the basics of computer hardware helps you make better decisions when it comes to performance, upgrades, and troubleshooting. With this knowledge, you’ll be able to optimize your setup for your specific needs—whether that’s gaming, work, or everyday tasks.